NOTE: Updated Feb 13, 2020 to include Windows Server 2019
More likely than not, if you’re using Group Policy to push out software installation or registry entries to client machines or servers on the domain, the particular policy settings may be different depending on the OS version or architecture.
Examples, Group Policy Objects may need to be filtered by:
- Desktop OS / Server OS
- Domain Controller / Non-Domain Controller
- 32-bit / 64-bit
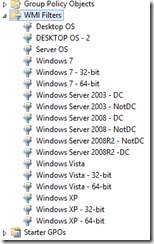
If you haven’t used Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) filters before, they show up in Group Policy Management at the bottom, between Group Policy Objects and Starter GPOs.
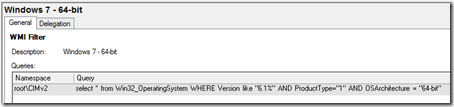
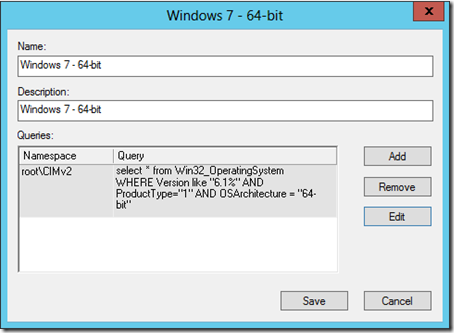
The WMI filters use a query to scope down the Group Policy Object applicability. Here’s what a typical WMI OS filter looks like:
WMI Win32_OperatingSystem ProductType Tips:
- ProductType 1 = Desktop OS
- ProductType 2 = Server OS – Domain Controller
- ProductType 3 = Server OS – Not a Domain Controller
WMI Win32_OperatingSystem Version Number Tips:
- 5.1 – Windows XP
- 5.2 – Windows Server 2003
- 5.2.3 – Windows Server 2003 R2
- 6.0 – Windows Vista & Windows Server 2008
- 6.1 – Windows 7 & Windows Server 2008 R2
- 6.2 – Windows 8 & Windows Server 2012
- 6.3 – Windows 8.1 & Windows Server 2012 R2
- 10.0 – Windows 10 & Windows Server 2016 & 2019
To create your own WMI filters, here is an updated list of WMI filter queries from Window XP – Windows 10 and from Server 2003 to Server 2019.
IMPORTANT DISCLAIMER:
Always test your Group Policies and WMI filters before deploying.
DESKTOP WMI QUERIES
ANY WINDOWS DESKTOP OS
- Any Windows Desktop OS – Version 1
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE ProductType = “1” - Any Windows Desktop OS – Version 2 (better for Win7 sometimes)
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (ProductType <> “2”) AND (ProductType <> “3”) - Any Windows Desktop OS – 32-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE ProductType = “1” AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Any Windows Desktop OS – 64-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE ProductType = “1” AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit”
WINDOWS XP
- Windows XP
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (Version LIKE “5.1%” or Version like “5.2%”) AND ProductType=”1″ - Windows XP – 32-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (Version LIKE “5.1%” or Version like “5.2%”) AND ProductType=”1″ AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows XP – 64-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (Version LIKE “5.1%” or Version like “5.2%”) AND ProductType=”1″ AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit”
WINDOWS VISTA
- Windows Vista
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.0%” AND ProductType=”1″ - Windows Vista – 32-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.0%” AND ProductType=”1″ AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows Vista – 64-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.0%” AND ProductType=”1″ AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit”
WINDOWS 7
- Windows 7
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.1%” AND ProductType=”1″ - Windows 7 – 32-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.1%” AND ProductType=”1″ AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows 7 – 64-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.1%” AND ProductType=”1″ AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit”
WINDOWS 8
- Windows 8
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.2%” AND ProductType=”1″ - Windows 8 – 32-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.2%” AND ProductType=”1″ AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows 8 – 64-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.2%” AND ProductType=”1″ AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit”
WINDOWS 8.1
- Windows 8.1
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.3%” AND ProductType=”1″ - Windows 8.1 – 32-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.3%” AND ProductType=”1″ AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows 8.1 – 64-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.3%” AND ProductType=”1″ AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit”
WINDOWS 10
- Windows 10
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “10.0%” AND ProductType=”1″ - Windows 10 – 32-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “10.0%” AND ProductType=”1″ AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows 10 – 64-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “10.0%” AND ProductType=”1″ AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit”
SERVER WMI QUERIES
ANY WINDOWS SERVER OS
- Any Windows Server OS
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (ProductType = “2”) OR (ProductType = “3”) - Any Windows Server OS – 32-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (ProductType = “2”) OR (ProductType = “3”) AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Any Windows Server OS – 64-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (ProductType = “2”) OR (ProductType = “3”) AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Any Windows Server – Domain Controller
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (ProductType = “2”) - Any Windows Server – Domain Controller – 32-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (ProductType = “2”) AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Any Windows Server – Domain Controller – 64-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (ProductType = “2”) AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Any Windows Server – Non-Domain Controller
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (ProductType = “3”) - Any Windows Server – Non- Domain Controller – 32-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (ProductType = “3”) AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Any Windows Server – Non-Domain Controller – 64-bit
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (ProductType = “3”) AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit”
WINDOWS SERVER 2003
- Windows Server 2003
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2%” AND ProductType<>”1″ - Windows Server 2003 – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2%” AND ProductType=”2″ - Windows Server 2003 – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2%” AND ProductType=”3″ - Windows Server 2003 – 32-bit – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2%” AND ProductType=”2″ AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows Server 2003 – 32-bit – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2%” AND ProductType=”3″ AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows Server 2003 – 64-bit – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2%” AND ProductType=”2″ AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows Server 2003 – 64-bit – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2%” AND ProductType=”3″ AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit”
WINDOWS SERVER 2003 R2
- Windows Server 2003 R2
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2.3%” AND ProductType<>”1″ - Windows Server 2003 R2 – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2.3%” AND ProductType=”2″ - Windows Server 2003 R2 – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2.3%” AND ProductType=”3″ - Windows Server 2003 R2 – 32-bit – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2.3%” AND ProductType=”2″ AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows Server 2003 R2 – 32-bit – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2.3%” AND ProductType=”3″ AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows Server 2003 R2 – 64-bit – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2.3%” AND ProductType=”2″ AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows Server 2003 R2 – 64-bit – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “5.2.3%” AND ProductType=”3″ AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit”
WINDOWS SERVER 2008
- Windows Server 2008
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.0%” AND ProductType<>”1″ - Windows Server 2008 – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.0%” AND ProductType=”2″ - Windows Server 2008 – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.0%” AND ProductType=”3″ - Windows Server 2008 – 32-bit – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.0%” AND ProductType=”2″ AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows Server 2008 – 32-bit – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.0%” AND ProductType=”3″ AND NOT OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows Server 2008 – 64-bit – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.0%” AND ProductType=”2″ AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit” - Windows Server 2008 – 64-bit – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.0%” AND ProductType=”3″ AND OSArchitecture = “64-bit”
WINDOWS SERVER 2008 R2
- Windows Server 2008 R2
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.1%” AND ProductType<>”1″ - Windows Server 2008 R2 – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.1%” AND ProductType=”2″ - Windows Server 2008 R2 – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.1%” AND ProductType=”3″
WINDOWS SERVER 2012
- Windows Server 2012
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.2%” AND ProductType<>”1″ - Windows Server 2012 – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.2%” AND ProductType=”2″ - Windows Server 2012 – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.2%” AND ProductType=”3″
WINDOWS SERVER 2012 R2
- Windows Server 2012R2
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.3%” AND ProductType<>”1″ - Windows Server 2012 R2 – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.3%” AND ProductType=”2″ - Windows Server 2012 R2 – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “6.3%” AND ProductType=”3″
WINDOWS SERVER 2016 *
- Windows Server 2016
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (Version LIKE “10.0.14393%”) OR (Version LIKE “10.0.16299%”) OR (Version LIKE “10.0.17134%”) AND ProductType<>”1″ - Windows Server 2016 – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (Version LIKE “10.0.14393%”) OR (Version LIKE “10.0.16299%”) OR (Version LIKE “10.0.17134%”) AND ProductType=”2″ - Windows Server 2016 – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (Version LIKE “10.0.14393%”) OR (Version LIKE “10.0.16299%”) OR (Version LIKE “10.0.17134%”) AND ProductType=”3″
WINDOWS SERVER 2019 *
- Windows Server 2019
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (Version LIKE “10.0.17763%”) OR (Version LIKE “10.0.18362%”) OR (Version LIKE “10.0.18363%”) AND ProductType<>”1″ - Windows Server 2019 – DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (Version LIKE “10.0.17763%”) OR (Version LIKE “10.0.18362%”) OR (Version LIKE “10.0.18363%”) AND ProductType=”2″ - Windows Server 2019 – non-DC
SELECT * FROM Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE (Version LIKE “10.0.17763%”) OR (Version LIKE “10.0.18362%”) OR (Version LIKE “10.0.18363%”) AND ProductType=”3″
* A few notes about the “OR” operator:
First – The reason for the “OR” statements in Server 2016 and Server 2019 WMI Query Filters is because there are multiple builds, as shown in the table below. These multiple builds are part of Microsoft’s Windows as a service (Waas) plan.
Second – “Or” combines two conditions. When more than one logical operator is used in a statement, the OR operators are evaluated after the AND operators. (Source)
| Major | Minor | Version | Build | Info | Released |
| 10 | 0 | 1607 | 14393 | 2016 RTM LTSC | 09/26/2016 |
| 10 | 0 | 1709 | 16299 | 2016 SAC | 10/17/2017 |
| 10 | 0 | 1803 | 17134 | 2016 SAC | 04/30/2018 |
| 10 | 0 | 1809 | 17763 | 2019 LTSC | 11/13/2018 |
| 10 | 0 | 1903 | 18362 | 2019 SAC | 5/21/2019 |
| 10 | 0 | 1909 | 18363 | 2019 SAC | 11/12/2019 |
Helpful OS Term Abbreviations
- LTSC – Long-Term Servicing Channel
- RTM – Release to Manufacturing
- SAC – Semi-Annual Channel
- SSU – Servicing Stack Updates